
Bits vs. Bytes
What do all of these abbreviations have to do with my internet speed?
When it comes to your internet, do you know your bits from your bytes? What about your 10Mbps from 10MB? Your 5G from your 5GHz? Don’t worry, these terms can be complicated, but we’ll break them down in the guide below.
What are Megabits?
Bits are the smallest measure of data. What do these tiny pieces of data have to do with your internet speed? Broadband speed is usually measured in megabits per second or Mbps. A megabit equals 1 million bits, so the measurement Mbps is how many millions of bits of data can be sent per second. The higher the Mbps of your internet, the faster you will be able to work, surf, stream, and game.
Common internet speeds include:
- Up to 100 Mbps - upload and download speeds of 100 megabits per second are sufficient for an entire family to stream, surf or work at the same time.
- Up to 250 Mbps - provides even faster uploading and downloading speeds, which is ideal for frequent video conferencing, streaming, and gaming, especially if more than one device is uploading or downloading at the same time.
- Up to 1 Gbps (or 1,000 Mbps or 1 gig) - provides the fastest data transfer speeds available. This lightning-fast connection is only available over a fiber network like Luminate Broadband. With 1 gig, you can use dozens of devices, download huge files quickly and stream at the very highest speeds.

Are Megabits the Same as Megabytes?
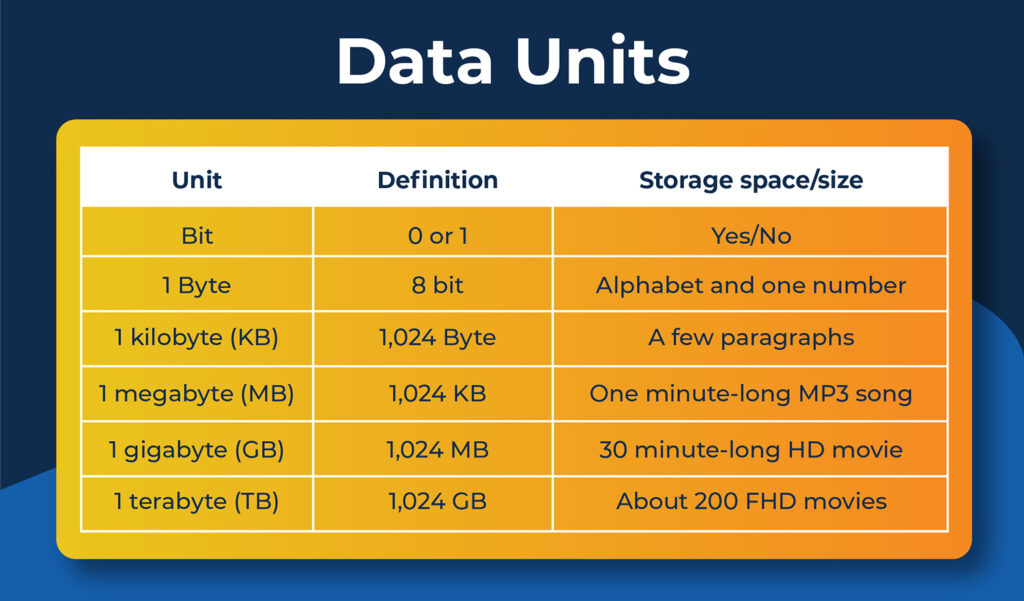
When seeking out an internet plan, you might also come across the abbreviation MB, which stands for megabytes. Megabits (Mb) and megabytes (MB) are not the same term, but they are related in that one byte is equal to 8 bits. However, it might be more useful for you to forget that information because the two terms are used to describe very different things when it comes to internet usage.
MB is a unit of measurement for data usage and storage. Here are a few ways that you’ll see bytes in your day-to-day data usage:
Data usage
The data that you use over your internet is measured in MB. One study found that most households in America used about 200GB (GB stands for gigabyte, which is equal to 1,000 MB) of data per month in 2018. That number increased significantly as people were working from home throughout the COVID shutdown. One reason is that video conferencing uses a lot of data to both upload and download video. By one estimation, a Zoom call uses up to 810 MB of data per hour. Many internet providers cap the amount of data that households can use each month, but Luminate offers unlimited data usage no matter which plan you choose.
Data storage
You might see options for cell phone and computer storage such as 64 GB, 128 GB, and 256 GB. These measurements mean the device can hold many thousands of megabytes in operating systems, apps, and photos.
Bytes are also used to describe file size. A Word document might take up about 100KB (KB stands for kilobyte, 1,000 KB equals 1 MB) of space, and a one-hour video file could take up more than 1GB of storage.
What is a 5G network?
When it comes to bits and bytes, what does G have to do with anything? The G in 5G stands for a specific generation of connection, which means that the 5G network is the 5th generation of the wireless and broadband network. This generation is the fastest and offers more opportunities for digital advancement.
Here’s how 5G compares to the other generations, per the FCC:
1G allowed voice calling.
2G allowed messaging.
3G allowed for internet and video.
4G broadened video and data usage capabilities.
5G is the fastest and most advanced connection (as of now).
Is 5G the same as 5 GHz?
In 5G, the G stands for generation. In 5 GHz, the GHz stands for gigahertz, which measures frequency. Wi-Fi signals in your home are sent from your router to your device through radio frequencies. When connecting to your Wi-Fi from your device, you might see that there is an option between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Some people think that 5 GHz is automatically better, but it’s not necessarily true; in reality, it depends on how close you are to the router. Wi-Fi sent over the 5 GHz signal is faster but does not have a long range. Wi-Fi sent over the 2.4 GHz is weaker, but its range extends further.
No matter what you need your internet to do, Luminate’s fiber-fast network can handle it. Understanding the ins and outs of data with the help of our trusty bits vs. bytes guide can help you make more informed decisions about which internet plan is for you.


